China Economic Quarterly Q2 2022
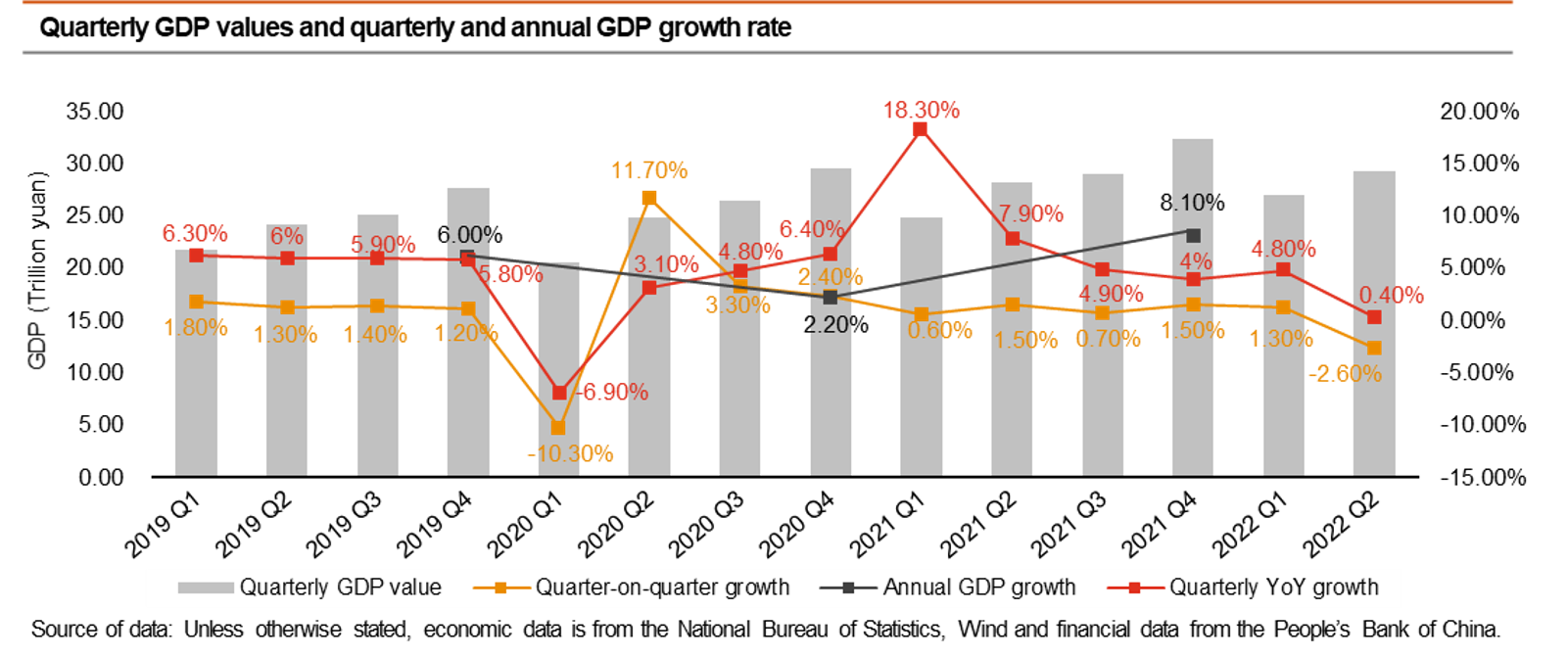
GDP increase was stunted due to new COVID-19 outbreaks, 0.4% in Q2 and 2.5% in H1. Full economic recovery in H2 might face headwinds.
This issue provides an overview of the macroeconomic trends in Q2 2022, some policy updates and hot topic analysis.

Highlights
Here are some macro-economic highlights:
- Total GDP reached 56 trillion yuan with 2.5% growth in H1
- Total fixed asset investment reached 27 trillion yuan, a 6.1% increase
- Total real estate investment reduced by 5.4% to 6.8 trillion yuan
- PMI rebounded to above 50% in June
- Industrial added values grew 3.4% in H1
- Total retail sales of consumer goods decreased by 0.7% to 21 trillion yuan
- Imports and exports increased by 9.4% to 19.8 trillion yuan
- PPI increased by 6.1% and CPI went up 2.5% in June
Policy updates
Growth of aggregate financing to the real economy reached by 10.8% in H1
According to the People’s Bank of China (PBoC), supportive measures for the real economy were further strengthened to stabilise economic growth in H1. The total aggregate financing to the real economy (AFRE) increased by 21 trillion yuan, 3.2 trillion yuan more YoY.
Fiscal revenue decreased by 10.2% while fiscal spending grew by 5.9%
In H1, fiscal revenue dropped by 10.2% YoY and reached 10.52 trillion yuan, as a result of new COVID-19 outbreaks, according to the Ministry of Finance. Excluding value-added tax credit refunds, fiscal revenue grew by 3.3%. Meanwhile, the national public budget expenditure increased by 5.9% to 12.89 trillion yuan.
Hot topic analysis: The progress of digital yuan and internationalisation of the Chinese currency
The digital yuan, also known as e-CNY, has made remarkable progress since its pilot scheme launch in May 2020. China continues to expand the scope of its pilot tests and explore applications of the domestically-invented Digital Currency and Electronic Payment (DCEP) network. According to the People’s Bank of China (PBoC), the tests have extended to 21 regions in 15 provinces and cities, including municipalities directly under the Central Government such as Beijing and Shanghai.
As a sequel to PwC’s report, “The business implications of China’s digital RMB”, this report will review the progress made in the past two years and examine the potential path to internationalisation for China’s digital currency, as well as its implications for the business sector.
Implications and opportunities
- In particular, the financial industry, including wealth management, loan and insurance services, has accepted and applied the digital yuan since the beginning of 2022. Within the industry, digital yuan loans and credit cover a range of products such as personal consumption loans, automobile consumption loans, and manufacturing loans, among others.
- Furthermore, the scope of digital yuan application is continuously developing vertically. Its application expanded from offline to online, extending from the consumer market to the business sector.
- In terms of international payments, the digital yuan is likely to extend extensively in the growing 2 trillion yuan cross-border e-commerce market. Shenzhen launched a trial for cross-border digital yuan payments, targeting Hong Kong residents. Digital yuan may play an active role in cross-border financial reform and co-operation between Hong Kong, Macau, and other Greater Bay Area cities.
- The digital transformation of currency will certainly improve overall economic efficiency, but accompanying issues such as privacy protection and cybersecurity will become a greater concern. These challenges can add to additional costs for many businesses but they can also create revenue opportunities for others.
Contact us
Managing Partner - Markets, PwC China
Tel: +[86] (10) 6533 2838 / +[852] 2289 8288